
Grading Diamonds - the Four C's : Cut, Clarity, Color and Carats
How a Diamond's Qualities are Graded
A diamond certificate is not the same thing as an appraisal. A certificate describes the quality of a diamond, but it does not place a monetary value on the gem. An appraisal places a monetary value on your diamond, but does not certify the quality of the diamond.
GIA - Gemological Institute of America, AGS - American Gem Society, and EGL - European Gemological Laboratory are the three most widely known and respected diamond grading laboratories in the world. Each of the grading laboratories have developed a very similar nomenclature for identifying the 4 C's of diamonds. The 4 C's stand for Carat, Color, Clarity, and Cut. We will also discuss the Shape of diamonds.
Carat Grading
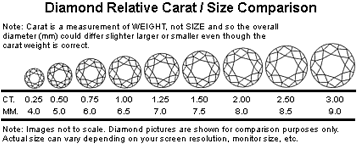 The weight or size of a diamond is measured in carats. A carat is 0.2 grams or 200 milligrams and is always referenced within 2 decimal points. This is a highly accurate grading scale used to determine the weight or size of a diamond.
The weight or size of a diamond is measured in carats. A carat is 0.2 grams or 200 milligrams and is always referenced within 2 decimal points. This is a highly accurate grading scale used to determine the weight or size of a diamond.
Color Grading
All diamonds are compared against to an internationally accepted set of master stones and ranges from totally colorless (D) to pale yellow or brown color (Z). Brown diamonds darker than K color are usually described using their letter grade, and a descriptive phrase, for example M Faint Brown. Diamonds with more depth of color than Z color fall into the fancy color diamond range.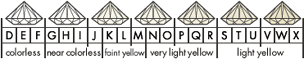
Color grades D through F are naturally the most valuable and expensive because of their rarity. Color G through I will show virtually no visible color to the untrained eye. Selecting the right jewelry to mount the diamond in can minimize color grade J through M.
The coloration of diamonds can be caused by several factors. Impurities trapped in the diamond during its formation, the crystal lattice structure of the diamond, and the exposure to radiation can all lead to the wide verity of colors available in diamonds.
Clarity Grading
Clarity is determined by the number of blemishes on the surfaces of the diamond and the number of inclusions such as air bubbles, cracks, and foreign material inside of the diamond. When both terms are being referenced the term defects is usually referenced. Nature rarely produces anything that is with out defects and this hold true for diamonds. Most diamonds will have some type of defect or flaw.
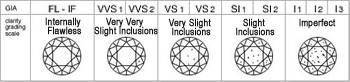 When grading the Clarity of a diamond it is necessary to observe the number and the nature of any internal defects in the stone. The size and position of the defects are also taken into account.
When grading the Clarity of a diamond it is necessary to observe the number and the nature of any internal defects in the stone. The size and position of the defects are also taken into account.
- A diamond is said to be Internally Flawless (I.F) when it presents no internal defects under 10x magnification by an experienced eye of laboratory gemologists.
- A diamond is said to be Very Very Slightly included (V.V.S.1 to V.V.S.2) when it presents defects that are very difficult to locate under 10x magnification.
- A diamond is said to be Very Slightly Included (V.S.1 to V.S.2) when it presents defects that are difficult to locate under 10x magnification.
- A diamond is said to be Slightly Included (S.I.1 to S.I.2) when it presents defects that are easy to locate under 10x magnification.
- A diamond is said to be Imperfect (P.1 to I.1) when it presents defects that are hard to locate with the naked eye.
- A diamond is said to be Imperfect (P.2 to I.2) when it presents defects that are easy to locate with the naked eye.
- A diamond is said to be Imperfect (P.3 to I.3) when it presents defects that are very easy to locate with the naked eye.
Cut Grading
The symmetry and proportions of a diamond cut determine the life, brilliance and light dispersion. If any of these cutting factors are below standard then the appearance of the diamond will be adversely affected.
The cut of a diamond has nothing to do with the shape of the diamond. The cut refers to the diamond's reflective qualities. A good cut gives the diamond it brilliance or the ability to handle light in a pleasing fashion. The brightness will seem to come from the very heart of a diamond.
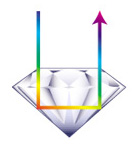 When a ray of light touches the surface of a diamond, part of the light is reflected back, this is external reflection. The rest of the ray penetrates the stone and is then reflected toward the center of the diamond. This is known as refraction. The ray of light is reflected to the surface, where it is seen as the colors of the spectrum. This is known as dispersion.
When a ray of light touches the surface of a diamond, part of the light is reflected back, this is external reflection. The rest of the ray penetrates the stone and is then reflected toward the center of the diamond. This is known as refraction. The ray of light is reflected to the surface, where it is seen as the colors of the spectrum. This is known as dispersion.
If light enters the diamond through to top or table and then leaks out from the sides or bottom instead of reflecting back to the eye, then the diamond will seen to have less brilliance and fire. A diamonds cut is the most important of the four Cs. If all of the rest of the grading scale is at the higher end of the spectrum and the cut has been utilized to maximize the size of the diamond then a very poor quality stone will be the result. Happily this trend in size instead of quality is no longer prevalent in the diamond market. Today standard mathematical algorithms are used to determine the best cut for any shape diamond.
Shape
The shape of diamond will fall into one of several standard categories but there are many variations on each standard categories. Basic categories include Round, Emerald, Pear, Heart, Marquise, Oval, and Princess cuts.
Round
The standard for the diamond shape and is used in most engagement rings.
Emerald
Rectangular or square step cut with diagonally cut corners. Usually has 2 to 4 rows of parallel facets to the center of the stone. A very popular style of cut used for Emeralds hence the name.
Pear
Pear or teardrop in shape and may or may not have a large flat surface in the center of the stone. This stone is usually cut to have about 56 to 58 facets.
Heart
Heart in shape and if a shield shaped cutlet is present (flat center) then it will usually have 32 crown facets. If no culet is present then 24 pavilion facets is the norm.
Marquise
Oval in shape with curving sides and pointed ends and was developed in France in the mid 1700s. May have been named after the Marquise de Pompador, who was a mistress of King Louis XV.
Oval
Oval in shape and covered with triangular facets.
Princess Cuts
Very popular square or modified rectangular shape. There are many variations of crown and pavilion facets cuts on the market.

 Some time ago you both made a promise. A promise to each other. Now it’s time to recognise that you both meant that promise, and that now you both still mean it.
Some time ago you both made a promise. A promise to each other. Now it’s time to recognise that you both meant that promise, and that now you both still mean it.